Introduction
Understanding Asphalt Production
Types of Asphalt Plants
- Batch Mix Asphalt Plant
- Produces asphalt in specific batch sizes.
- Allows precise control over mix specifications.
- Suitable for projects requiring different asphalt types.
- Preferred for high-quality asphalt with variations in composition.
- Drum Mix Asphalt Plant
- Continuous production process with a steady output.
- Ideal for large-scale infrastructure projects.
- More energy-efficient than batch plants.
- Lower initial investment cost and higher production rates.
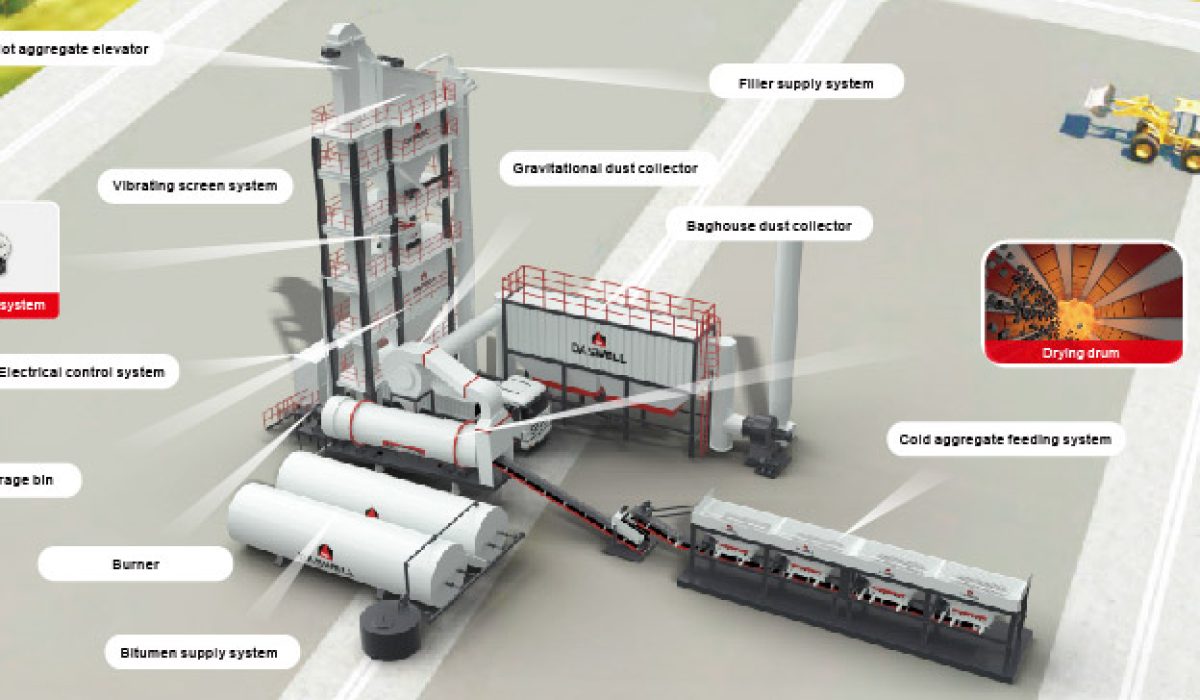
Key Components of an Asphalt Plant
An asphalt plant consists of several essential components, each playing a crucial role in the production process:
- Cold Aggregate Feeder Bins
Aggregates such as gravel, sand and stone are stored in separate bins before being transferred to the drying drum. The bins control the flow rate and proportion of aggregates used in the mix, ensuring a balanced composition.
- Conveyor System
A conveyor belt transports aggregates from the feeder bins to the drying drum. It ensures a steady supply of materials for continuous production and prevents bottlenecks in the production process.
- Drying Drum
The drying drum removes moisture from aggregates using high-temperature heating. Proper drying is essential for producing high-quality asphalt, as excess moisture can lead to improper binding and a weaker final product.
- Burner
The burner provides the heat required for drying and mixing. It operates on fuels such as diesel, natural gas, or heavy oil. Modern burners are designed to optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions.
- Dust Collection System
Modern asphalt plants use dust collection systems to capture fine particles and prevent air pollution. This improves environmental compliance, maintains a clean workspace and ensures workers’ safety.
- Mixing Unit
The mixing unit combines heated aggregates with bitumen and filler materials. In batch plants, this process occurs in intervals, ensuring a precise blend, while in drum mix plants, it happens continuously, making it more efficient for high-volume production.
- Storage Silos
Finished asphalt is stored in insulated silos before being transported to construction sites. These silos help maintain the asphalt’s temperature and prevent premature cooling, allowing for efficient delivery and application.
Understanding Asphalt Production
The Asphalt Production Process
The asphalt manufacturing process follows a structured workflow to ensure efficiency and quality.
Step 1: Aggregate Feeding and Drying
Aggregates are fed into the drying drum, where they are heated to remove moisture. Proper drying ensures a uniform and durable asphalt mix, preventing potential issues in the final application.
Step 2: Mixing with Bitumen and Fillers
The dried aggregates are mixed with bitumen and filler materials in the mixing unit. The temperature is carefully controlled to maintain consistency, ensuring that the asphalt mix meets industry standards.
Step 3: Quality Control and Testing
Samples of the asphalt mix are taken for testing to ensure compliance with project specifications and industry regulations. This process guarantees a reliable and high-performance final product.
Step 4: Storage and Transportation
The final product is stored in silos and transported to construction sites using insulated trucks to prevent cooling and segregation. Proper storage ensures that the asphalt remains workable until it is applied.
Environmental Considerations in Asphalt Production
Benefits of Modern Asphalt Plants
Advancements in asphalt plant technology have led to several advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Advanced heating systems reduce fuel consumption and operational costs.
- Environmental Compliance: Strict emission control mechanisms ensure plants meet regulatory standards.
- High-Quality Output: Automated control systems ensure consistent mix quality and reduce material wastage.
- Increased Productivity: Continuous production capabilities enhance efficiency, reducing project delays and meeting tight deadlines.
Key Areas Where Asphalt is Utilized
Asphalt produced in plants is used in a wide range of industries and functions, including:
- Road Construction: Highways, urban roads and rural paths.
- Airport Runways: Durable surfaces capable of withstanding heavy aircraft traffic.
- Parking Lots: Commercial and residential parking areas.
- Bridges and Overpasses: Flexible material that can withstand structural movement.
- Industrial and Residential Paving: Smooth, durable surfaces for driveways, sports courts and industrial yards.
Maintenance and Longevity of Asphalt Plants
To ensure long-term operational efficiency, asphalt plants require regular maintenance, which includes:
- Routine Inspections: Checking conveyor belts, burner systems and storage silos for wear and tear.
- Cleaning Dust Collection Units: Ensuring emission control systems function optimally.
- Lubrication of Moving Parts: Preventing equipment failure and extending plant life.
- Calibration of Mixing Systems: Maintaining consistency in asphalt composition.
Conclusion
Asphalt plants are essential for producing high-quality paving materials for roads and infrastructure projects. Understanding their operation, components and production process helps industry professionals optimize efficiency and maintain quality standards. Modern plants are designed with environmental and efficiency considerations, ensuring cost-effective and sustainable production.
With continuous advancements in asphalt technology, the industry is evolving toward more efficient, eco-friendly and high-performance solutions. MACMIX remains at the forefront of asphalt production, offering innovative solutions tailored to meet the demands of today’s infrastructure needs.
For more information about asphalt plant operations or to explore our solutions, contact MACMIX today!